Research
Working Papers
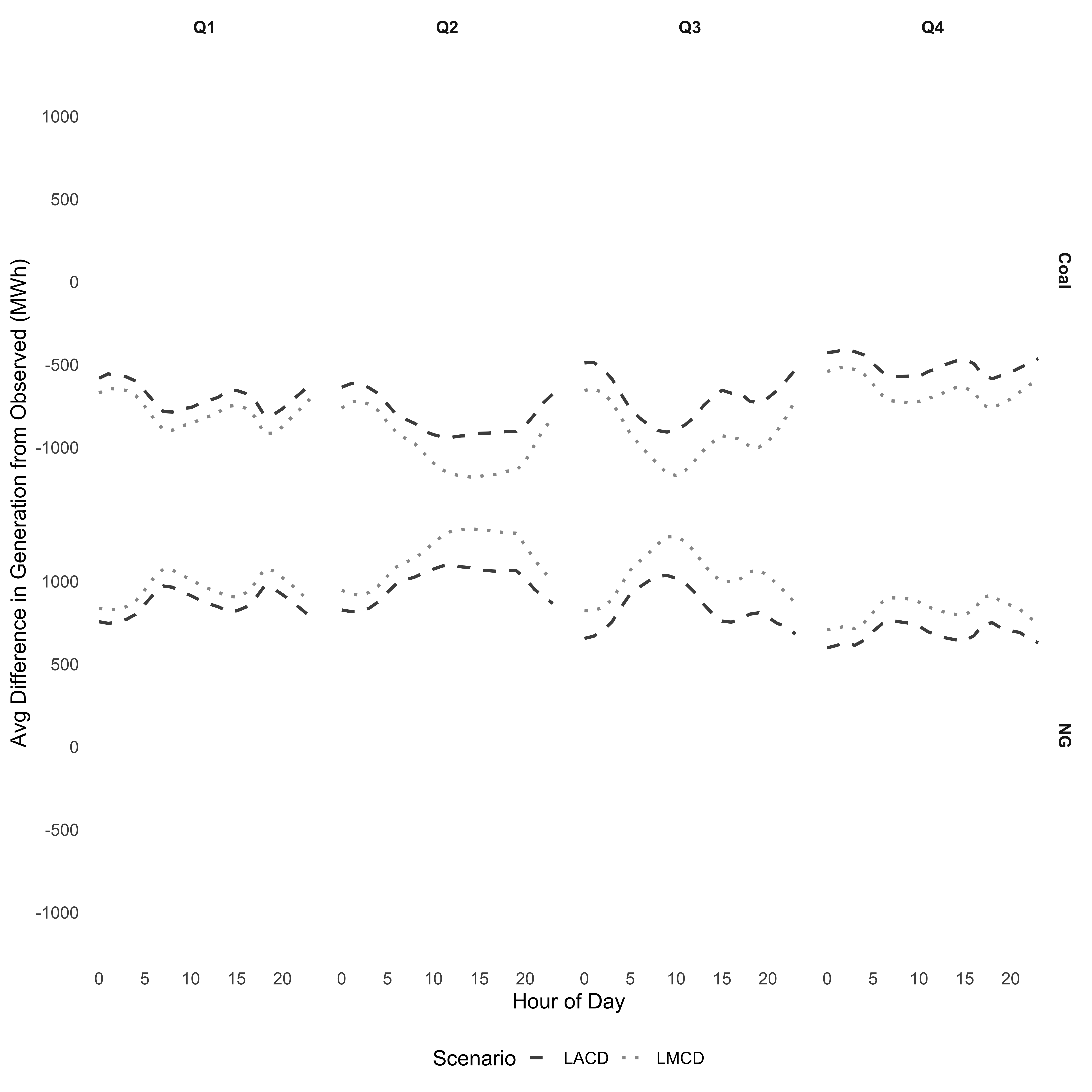
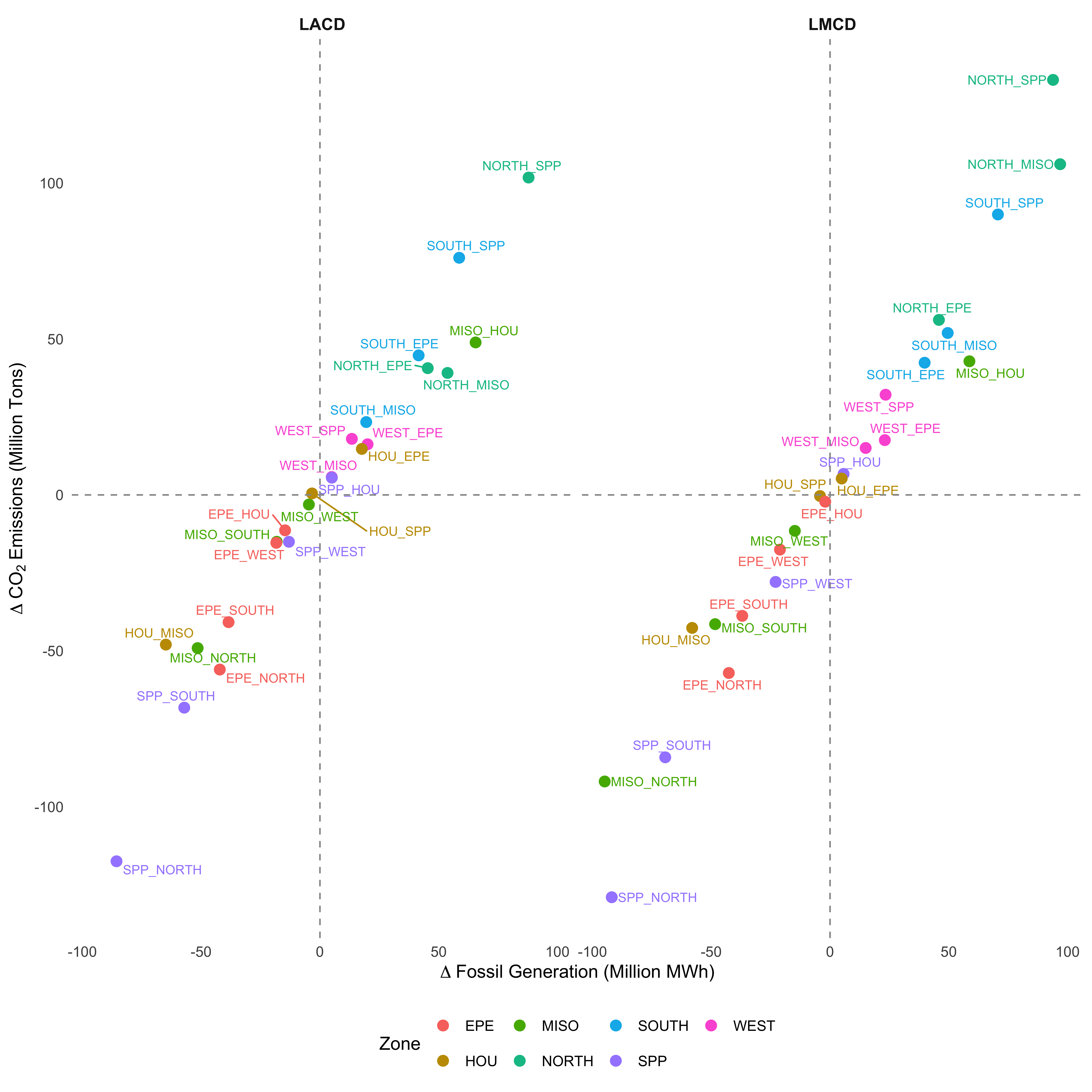
Lone Star Grid: The Impact of Texas Electricity Interconnection (with J. Scott Holladay) Draft
Abstract
This paper evaluates the economic and environmental costs of Texas maintaining an isolated electricity grid. We build a least average cost dispatch model to characterize the supply of electricity and simulate counterfactual integration scenarios. We find that Texas's largest population zones connected with neighboring states to the East results in reductions of generation costs of $100M annually. We also show that accounting for fixed costs in the dispatch model allocates generation to units with lower average fixed costs than under least marginal cost dispatch. This change in allocation along the margin results in large differences in emissions impacts. We find that some interconnection scenarios decrease the social cost of emissions by up to $360M annually, while others result in higher emissions. In case study for one proposed interconnection, we show that generation and revenues shift to the Texas zone. We also show that reductions in costs of maintaining reliability are about as much as generation cost reductions.
Works in Progress
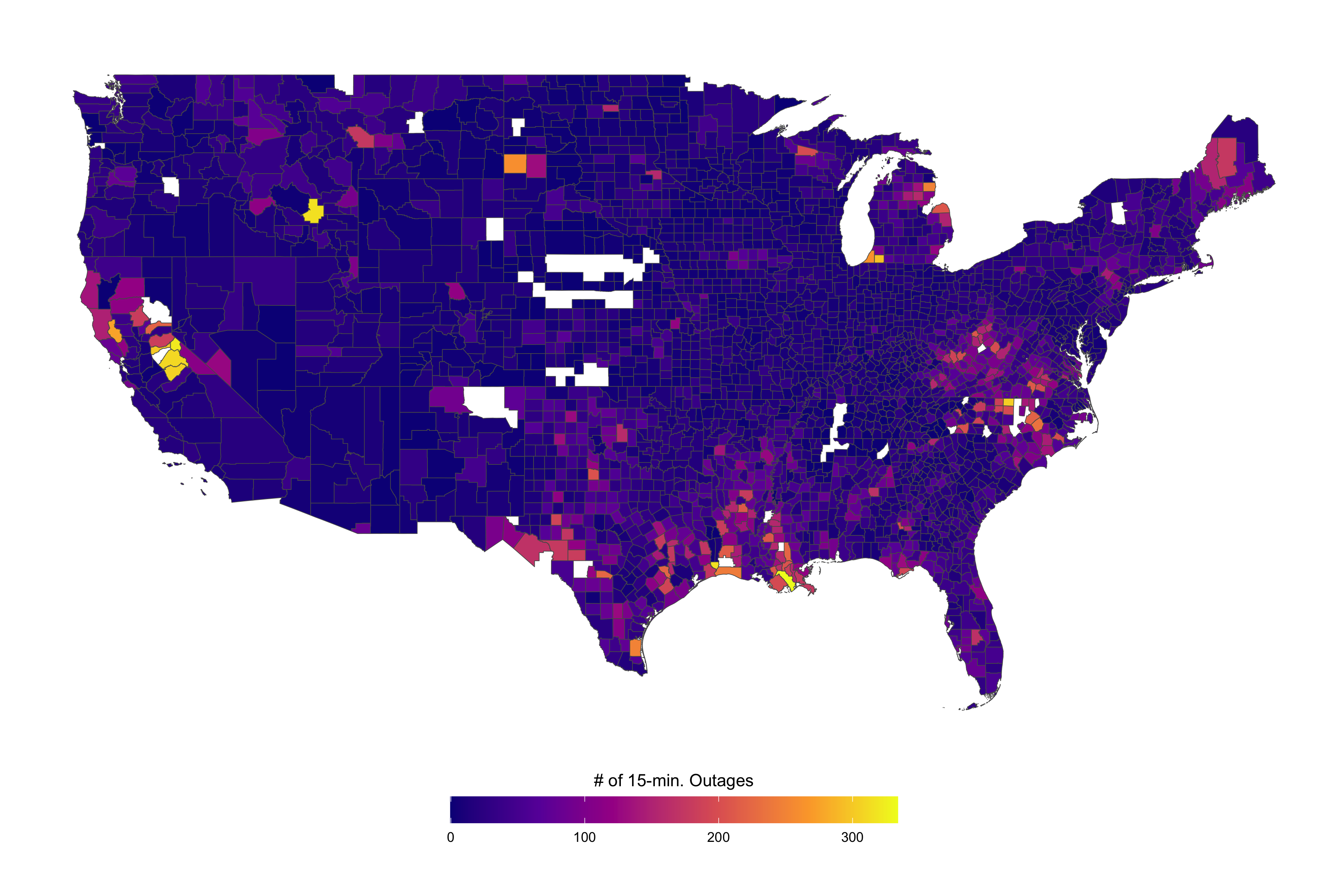
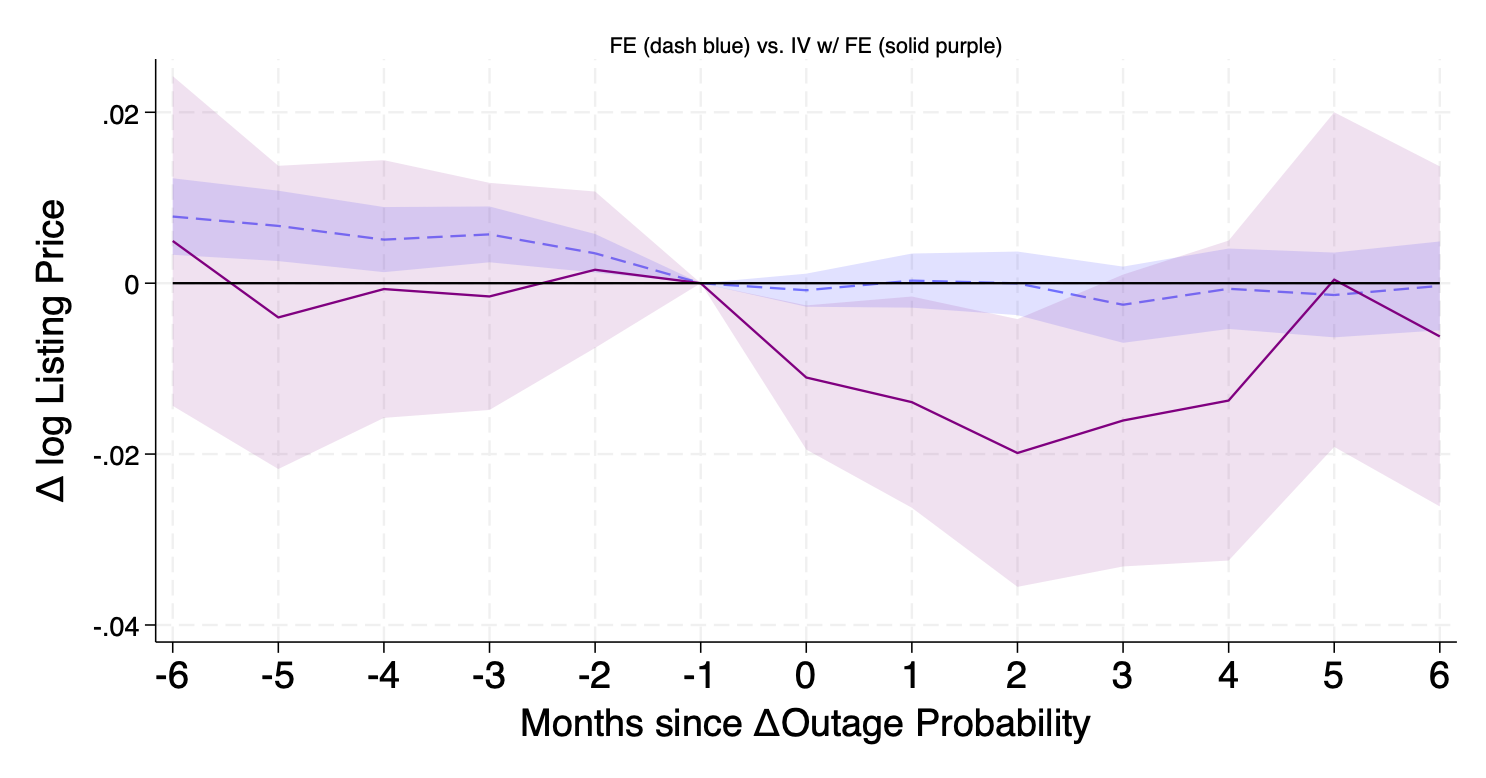
Electric Shocks: The Short-run and Long-run Impacts of Power Outages on the Housing Market
Abstract
Power disruptions are costly to households. How do consumers value power reliability disruptions? I exploit the variation in daily lightning strikes to provide new evidence on the capitalization of power reliability into home values. Ground lightning strikes lead to voltage fluctuations, damage to the electricity distribution network and power outages. Increases in lightning density (strikes per square mile) is associated with increased outages and decreases in county-level housing prices. I find that the average marginal willingness to pay for a 1 unit reduction in annual outages is about .37% of home price. I also evaluate the short-run impacts of power reliability shocks on short-run housing inventory outcomes. I find that a 10% increase in probability of experiencing at least one monthly outage is associated with as much as a .2% decrease in median listing price.
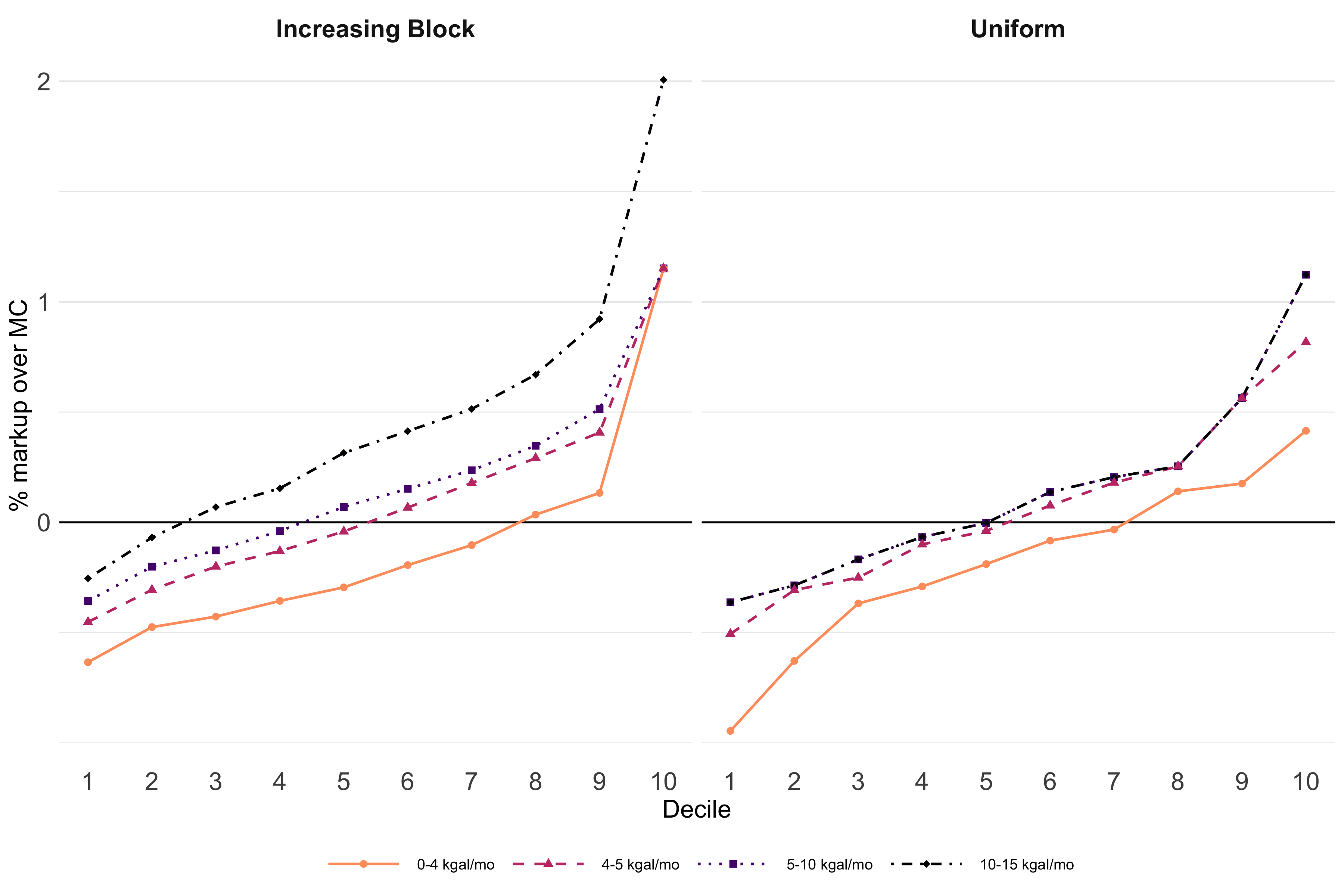
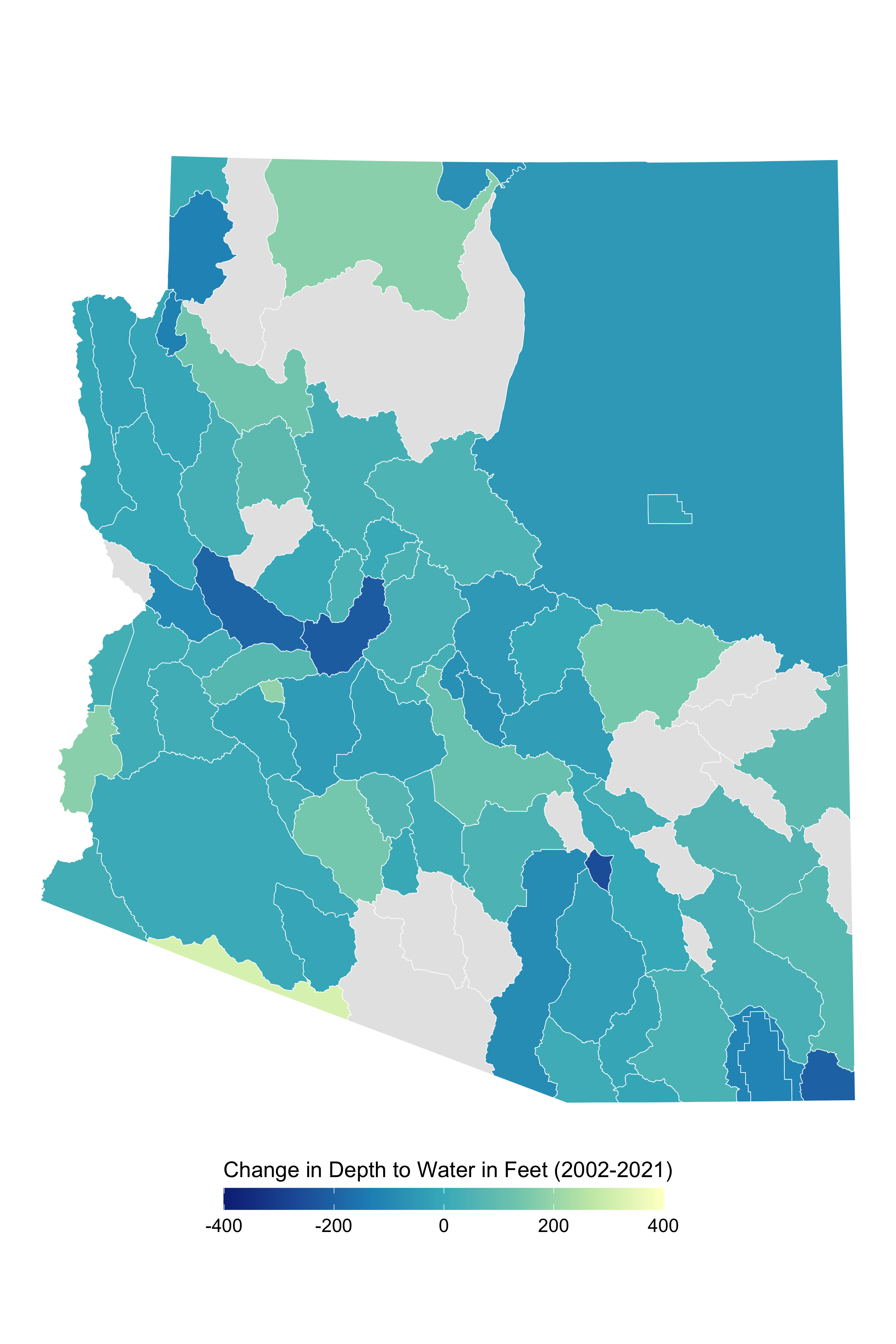
Rate Structures and Resource Rents in Municipal Water Pricing
Abstract
Several studies have analyzed how different rate structures and water utility characteristics influence equity, efficiency, and cost-recovery. The degree to which utilities incorporate the natural capital value of water into rates and costs is relatively unexplored. Using a simple model of dynamic water allocation suggests that increasing block rates reflect the scarcity value of water better than uniform volumetric rates. I construct a novel data set of nearly 200 utilities in Arizona to parameterize the model and analyze how rate structure and utility characteristics impact the extent to which resource rents are reflected in rates.